Inspiration Station: Sustainable housing ideas
/Found a gem of a website the other day called The Independent Patriot; a kind of step-by-step living guide to worst-case-scenario preparedness. The site, while a bit conspiratorial and fatalistic, features everything from information on long-term survival to food production and storage. "Wow" factor of peering into a fallout-shelter mentality aside, this guy's take on sustainable housing is downright inspirational.
Straw bale houses, buildings made out of old tires, rainwater catchment and graywater systems: you name it, this guy has outlined it. Great food for thought.
Click here to get a peek at the new frontier of sustainable living
(information is also pasted below).
Energy Efficient Structures

Monolithic domes provide superior insulation and protection from the elements, while giving the owner greater flexibility with interior construction. They can also provide and increased level of security when properly designed. These homes are compatible with passive and active solar systems, natural lighting, and underground cooling tubes. This style of home should be a top choice for people interested in independent living and home security. A monolithic dome is not typical "dome home." These domes are constructed by forming a ring-shaped foundation and attaching a flexible PVC "airform" which is then inflated to make the shape of the house. Several inches of polyurethane foam are then sprayed onto the inside of the dome, followed by steel rebar and several inches of concrete. The outside can also be coated with chain link and stucco to make an impermeable, fire-proof, hurricane-proof, earthquake-proof dome structure that is extremely well-insulated and provides an interior space with no supporting beams.
The structures can come in several different shapes and sizes. each airform is custom designed and fabricated. The cost of construction is similar to conventional construction, but the energy and maintenance savings can be substantial - especially in extremely hot or cold climates. These structures can be earth-bermed or covered with vines. Monolithic domes with stucco on the outside and 3"-4" of shotcrete on the inside also provide increased protection from small-arms fire.

Earth-sheltered homes range from homes with earth pushed up against the walls to homes that are entirely underground. Typically, an earth-sheltered home is set into a hill with earth on three sides and on top. The front is usually exposed to the south. The main advantage of an earth-sheltered home is the insulation offered by the thick covering of earth. Earth-sheltered homes maintain a constant 60-degree temperature, year-round, in hot or cold climates. They can be easily heated, and will hold the heat, due to the thick insulation.
Earth-sheltered homes have comparable construction costs to conventional homes, but cost far less to maintain. With proper use of skylights and windows on the southern exposure, they can have the interior appearance of a conventional home.
Insulating Concrete Forms (ICF) allow you to build a conventional-looking home with reinforced, double-insulated concrete walls. The forms for the walls are made of insulation "blocks" that are stacked and bound together. The space between the foam insulation is where the concrete is poured. The forms are placed over steel rebar and all plumbing and electrical is run through the walls before the concrete is poured. ICF blocks offer several ways of attaching sheetrock or wood paneling. Almost any type of exterior surface can be applied. The walls are thicker than a typical home, but they also provide much better insulation and strength. Multiple-story homes can be built with ICF.

Straw-bale homes offer a unique twist on highly-insulated structures. The main building component is straw, and the walls are at least two feet thick. The straw makes the building extremely well-insulated, and gives a "soft" feel to the corners. Straw-bale homes can either have load-bearing straw walls, or they can be framed and filled in with straw bales. All utilities are run through the walls as the bales are stacked. Bales are impaled on steel rebar for stabilization. The walls are typically covered with plaster or stucco. If properly sealed and plastered, they will not have problems with water, but high humidity can be an issue, since the water vapor can work its way into the straw. There is no increased risk of fire with the use of straw bales. Straw bales are extremely dense and provide little oxygen for fires to feed on. They are actually a better fire barrier than convention wood-framed walls.
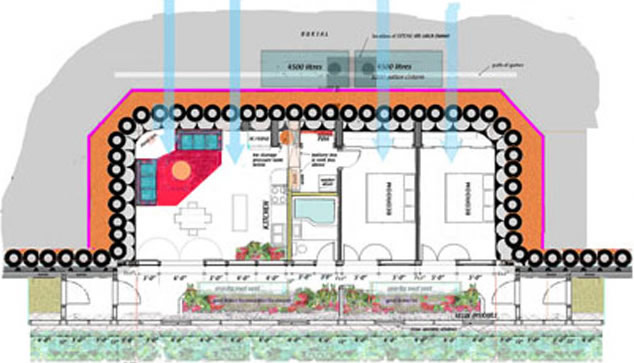
The Earthship concept goes beyond just home construction. It is aimed at providing a complete off-grid system that handles everything from water collection to gray water and sewage treatment. These homes are typically built into the side of a hill and use old tires as the primary wall building material. The tires are stacked like bricks and filled with rammed earth as each layer is laid. The buildings are oriented to the south, with a greenhouse wall that allows in light and lets you grow plants that help filter gray water. The integrated power and water systems make these homes very interesting. Some of these concepts could be used in conjunction with other earth-sheltered homes.























